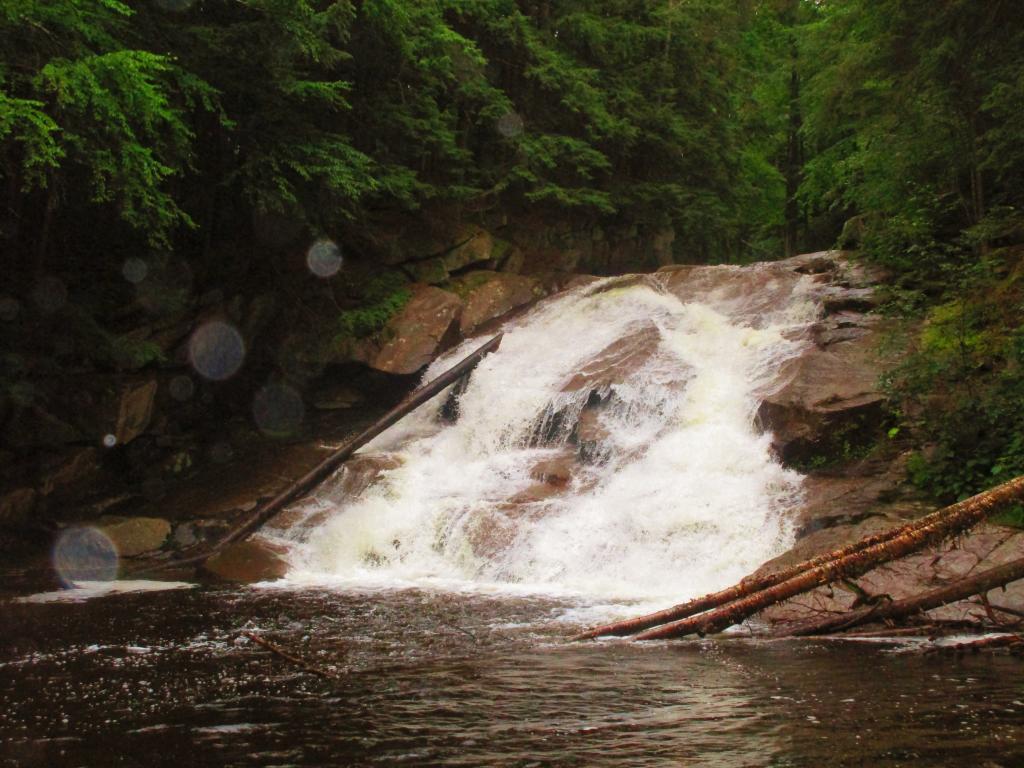
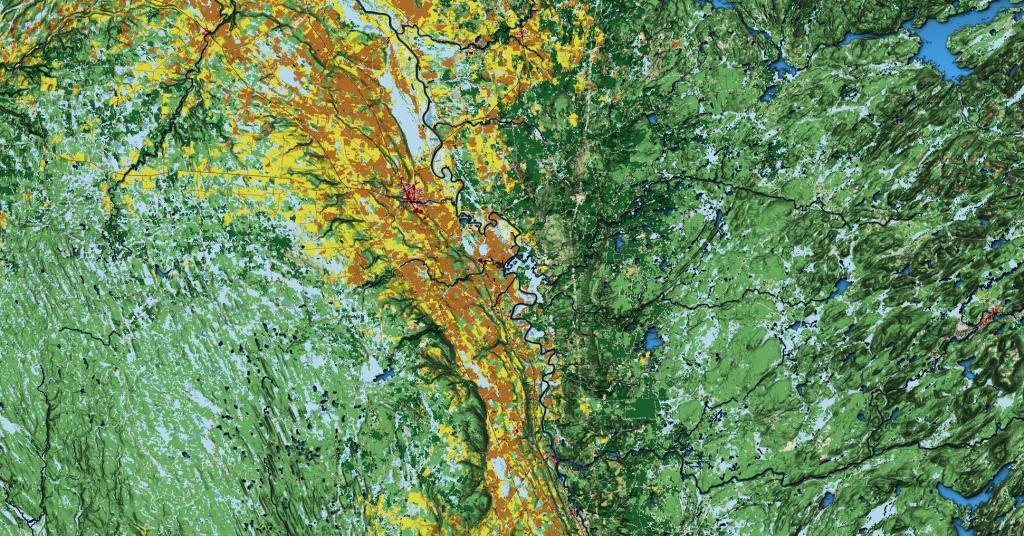
Today’s fodder is based on the text of the Adirondack Park State Land Master Plan that explains the Adirondack Scenic, Wild and Recreational Rivers System and the policies surrounding it quite well. — Andy
The Adirondack Park contains many rivers which, with their immediate environs, constitute an important and unusual resource. Classification of those portions of rivers that flow through state land is vital to the protection of existing free flowing streams. The classification system and the recommended guidelines specified below are designed to be consistent with and complementary to both the basic intent and structure of the legislation passed by the legislature in 1972 creating a wild, scenic and recreational rivers system on both state and private lands.
Definitions
A wild river is a river or section of river that is free of diversions and impoundments, inaccessible to the general public except by water, foot or horse trail, and with a river area primitive in nature and free of any man-made development except foot bridges.
A scenic river is a river or section of river that is free of diversions or impoundments except for log dams, with limited road access and with a river area largely primitive and undeveloped, or that is partially or predominantly used for agriculture, forest management and other dispersed human activities that do not substantially interfere with public use and enjoyment of the river and its shore. A recreational river is a river or section of river that is readily accessible by road or railroad, that may have development in the river area and that may have undergone some diversion or impoundment in the past.

Guidelines for Management and Use
Basic guidelines
1. No river or river area will be managed or used in a way that would be less restrictive in nature than the statutory requirements of the Wild, Scenic and Recreational Rivers Act, Article l5, title 27 of the Environmental Conservation Law, or than the guidelines for the management and use of the land classification within which the river area lies, but the river or river area may be administered in a more restrictive manner.
2. Rivers will be kept free of pollution and the water quality thereof kept sufficiently high to meet other management guidelines contained in this section.
3. No dam or other structure impeding the natural flow of a river will be constructed on a wild, scenic or recreational river, except for stream improvement structures for fisheries management purposes which are permissible on recreational and scenic rivers only.
4. The precise boundaries of the river area will be determined by the Department of Environmental Conservation, will be specified in the individual unit management plans for the river area or the areas, where the more restrictive guidelines of the particular area will apply) and with the following additional guidelines.
2. Access points to the river shore or crossings of the river by roads, fire truck trails or other trails open to motor vehicle use by the public or administrative personnel will normally be located at least two miles apart.
3. Other motor vehicle roads or trails in the river area will not be encouraged and, where permitted, will normally be kept at least 500 feet from the river shore and will be screened by vegetation or topography from view from the river itself.
4. The natural character of the river and its immediate shoreline will be preserved.
5. The following structures and improvements may be located so as to be visible from the river itself:
== fishing and waterway access sites;
== foot and horse trails and foot and horse trail bridges crossing the river; and,
== motor vehicle bridges crossing the river.
6. All other new, reconstructed or relocated conforming structures and improvements (other than individual lean-tos, primitive tent sites and pit privies which are governed by the regular guidelines of the master plan) will be located a minimum of 250 feet from the mean high water mark of the river and will in all cases be reasonably screened by vegetation or topography from view from the river itself.
7. Motorboat usage of scenic rivers will not normally be permitted but may be allowed by the Department of Environmental Conservation, where such use is already established, is consistent with the character of the river and river area, and will not result in any undue adverse impacts upon the natural resource quality of the area.
Recreational rivers
1. Recreational rivers and their river areas will be administered in accordance with the guidelines for management of wild forest areas (except where such rivers flow through wilderness, primitive or canoe areas, where the more restrictive guidelines of the particular area will apply) and with the following additional guidelines:
2. Where a recreational river flows through an intensive use area, structures, improvements and uses permitted in intensive use areas will be permitted, provided the scale and intensity of these intensive uses do not adversely affect the recreational character of the river and the river area.
3. The natural character of the river and its immediate shoreline will be preserved and enhanced.
4. The following structures and improvements may be located so as to be visible from the river itself:
== fishing and waterway access sites;
== docks;
== foot and horse trails and foot and horse trail bridges crossing the river;
== snowmobile trails, roads, and truck trails; and,
== motor vehicle bridges crossing the river.
5. All other new, reconstructed or relocated conforming structures and improvements (other than individual lean-tos and primitive tent sites which are governed by the regular guidelines of the master plan) will be located a minimum of 150 feet from the mean high water mark of the river and will in all cases be reasonably screened by vegetation or topography from view from the river itself.
6. Motorboat use of recreational rivers may be permitted, as determined by the Department of Environmental Conservation.

Designation of Wild, Scenic and Recreational Rivers
The application of the above definitions and criteria to rivers on state lands in the Park results in the current designation under this master plan of 155.1 miles of wild rivers, 511.3 miles of scenic rivers, and 539.5 miles of recreational rivers. A significant amount of private lands not covered by this master plan are included in these mileage figures. A brief description of these rivers and their classification is set forth in Chapter III.
| River |
Wild |
Scenic |
Recreational |
| Ampersand Brook |
|
8.6 |
|
| Ausable — Main Branch |
|
|
21.7 |
| Ausable — East Branch |
|
8.8 |
25.2 |
| Ausable — West Branch |
|
|
31.8 |
| Black |
|
6.8 |
5.8 |
| Bog |
|
6.2 |
|
| Boreas |
|
11.4 |
|
| Bouquet |
|
42.7 |
|
| Bouquet — North Fork |
|
5.9 |
|
| Bouquet — South Fork |
|
5.0 |
|
| Blue Mountain Stream (Trib. of Middle Branch, Grasse River) |
|
7.9 |
|
| Cedar |
13.5 |
13.0 |
10.4 |
| Cold |
|
14.5 |
|
| Deer |
|
5.7 |
|
| East Canada Creek |
19.3 |
|
|
| Grasse — Middle Branch |
|
12.9 |
|
| Grasse — North Branch |
|
25.4 |
|
| Grasse — South Branch |
36.1 |
4.2 |
|
| Hudson |
11.2 |
11.8 |
55.1 |
| Independence |
24.5 |
|
|
| Indian (Trib. of Hudson River) |
|
7.5 |
|
| Indian (Trib. of Moose River — South Branch) |
|
15.1 |
|
| Jordan |
|
15.7 |
|
| Kunjamuk |
|
7.1 |
9.1 |
| Long Pond Outlet |
|
16.3 |
|
| Marion |
|
4.4 |
|
| Moose — Main Branch |
|
15.0 |
11.0 |
| Moose – North Branch |
|
5.3 |
11.6 |
| Moose — South Branch |
|
|
33.6 |
| Opalescent |
|
10.4 |
|
| Oswegatchie — Main Branch |
|
|
14.9 |
| Oswegatchie — Middle Branch |
|
13.0 |
22.7 |
| Oswegatchie — West Branch |
|
7.2 |
6.3 |
| Otter River |
|
|
8.8 |
| Ouluska Pass Brook |
|
|
2.3 |
| Piseco Outlet |
|
|
3.8 |
| Raquette |
|
36.0 |
51.6 |
| Red |
|
8.0 |
|
| Rock |
|
6.4 |
1.3 |
| Round Lake Outlet |
|
|
2.4 |
| St. Regis — East Branch |
|
15.4 |
6.3 |
| St. Regis — Main Branch |
|
15.6 |
23.9 |
| St. Regis — West Branch |
|
31.5 |
5.5 |
| Sacandaga — East Branch |
11.3 |
|
12.6 |
| Sacandaga — Main Branch |
|
|
28.5 |
| Sacandaga — West Branch |
18.1 |
|
16.6 |
| Salmon |
|
|
11.6 |
| Saranac |
|
|
62.7 |
| Schroon |
|
|
63.9 |
| West Canada Creek |
7.4 |
17.1 |
9.1 |
| West Canada Creek — South Branch |
5.7 |
9.1 |
|
| West Stony Creek |
|
7.4 |
7.7 |
| Total
|
148.4
|
487.2
|
545.6
|