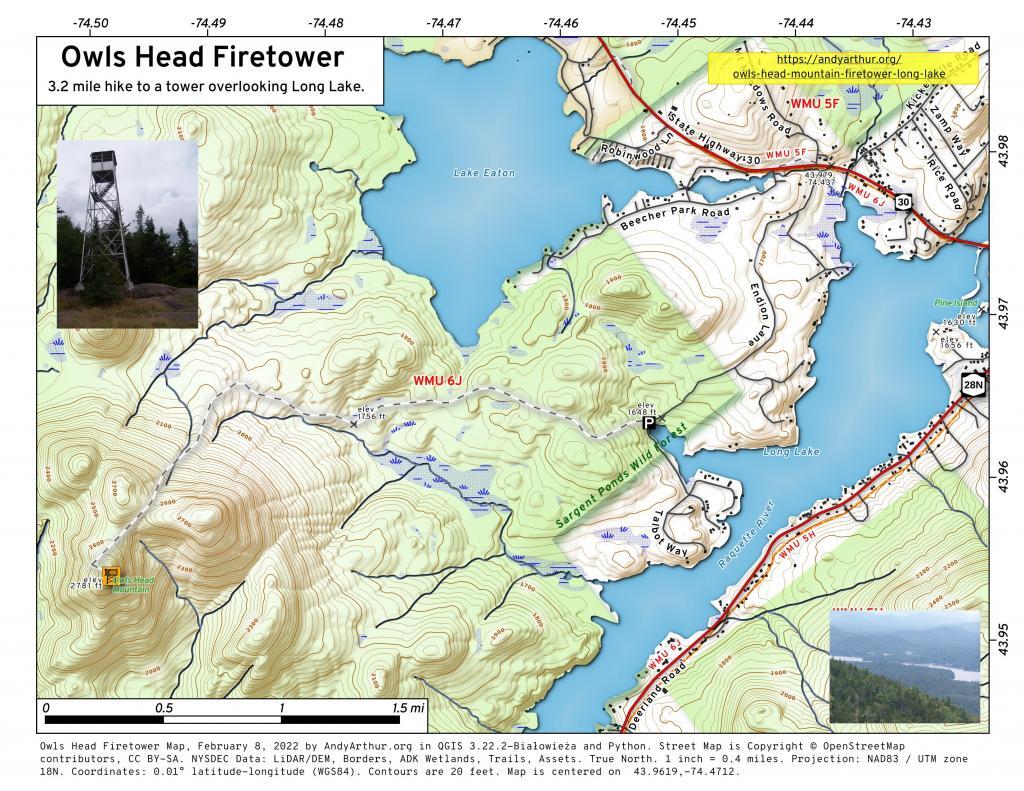
Today’s fodder was is an excerpt from “Moose River Plains Wild Forest Revised Draft Unit Management Plan/Draft Generic Environmental Impact Statement ‐ July 2010”, Appendix III, a NYS Department of Conservation Document that is in the public domain. As the DEC will probably eventually remove this from the internet, and because it is only in PDF I have decided to share it in the entirity in this blog post.
I have added some pictures I’ve taken over the years at Moose River Plains. I hope you find this interesting and helpful. – Andy
Past and Present Management Of Moose River Plains.
As Written By NYSDEC, Revised Draft Unit Management Plan
The State acquired an original tract of 9,000 acres in the heart of what is now the MRPWF before 1900. In 1948 the Conservation Department issued a permit allowing Gould Paper Company to use an existing wagon road known as the Kenwell Road to haul timber across State lands and to maintain a gate at the end of the road near Limekiln Lake to prevent public access. The Department acquired 15,710 acres surrounding Limekiln Lake from Gould in 1960, then another Gould parcel encompassing Lost Ponds and containing approximately 1,803 acres in 1962. An individual owner sold the State a parcel of 356 acres including Beaver Lake in 1963. The majority of what is now the MRPWF and the northern part of the West Canada Lake Wilderness was added to the Forest Preserve in 1963 when Gould Paper Company sold the State a tract of 50,970 acres stretching from Horn Lake on the west to Manbury Mountain on the east. Major subsequent additions included 602 acres surrounding Wakely Dam and the north end of Cedar River Flow from Finch, Pruyn and Company in 1964 and two large parcels acquired from International Paper Company: the 1,120‐acre Cellar Mountain parcel in 1986 and a tract of 9,925 acres south of Wakely Mountain in 1988. The larger parcel was acquired subject to a 1987 easement conveyed by IP to Hamilton County for the maintenance of the four miles of Cedar River Road which crossed the parcel. Appendix 25 contains an acquisition map.
A small parcel was acquired in 1981 along Route 28. This acquisition included access to the shore of Fourth Lake. However, there is no potential to develop any water access at this location. Appendix 15 contains a deed and sketch map for this parcel.

After this major acquisition, the Department took an active approach to the management of the area then referred to as the Moose River Recreation Area, a name which reflected the intent behind the purchase. From the beginning, the Department pursued the development of an extensive road system to provide public access to the remote interior for hunting, trapping, fishing and camping. An early Department report indicated that there were about 178 miles of primary gravel roads and an equal extent of secondary and winter roads throughout the former Gould lands. However none of the roads was suitable for public motor vehicle use without significant improvement. Minutes to a meeting of Department staff on December 9, 1963 included an estimated cost of $25,000 for the annual maintenance of 50 miles of roads and bridges. Starting in 1964, Division of Fish and Wildlife staff used heavy equipment to improve roads initially identified for public use. When the area first was opened to the public on October 23, 1964, the road connecting the Limekiln and Cedar River entrances had just been cleared by bulldozer, but remained difficult to traverse. In addition to the LLCR Road, the Rock Dam Road, Otter Brook Road and Sly Pond Loop were open to public use by permit for a total of about 30 miles. Fifty‐six parking areas were established along the road system. At the entrance gates, cars were assigned parking areas and travel was allowed only to and from those areas. The public were four‐wheel drive vehicles or tire chains. Pickups with slip‐on campers were permitted from the start, but because the roads were not yet suitable, trailers were not permitted.

In a road plan adopted in 1965, roads to be designated were divided into three categories. Twenty‐two miles would be first priority roads, open to all traffic; 30.5 miles would be second priority roads open only to fourwheel drive vehicles; and 7.5 miles would be administrative roads restricted to use by Department staff for crossing private property. In the first years after the area was opened to the public, access remained difficult because of the effects of weather on road conditions. In the summer of 1965, work needed to make the roads passable delayed opening until July 1. In order to minimize fire danger and facilitate the disposal of trash, the public was allowed to camp only in areas adjacent to the roads and for a maximum of 3 days. Trash receptacles eventually were provided at most campsites and Department staff collected trash twice a week through the 1970s. The trash was deposited at a dump site south of the LLCR Road east of Helldiver Pond.

The road crew worked steadily year by year to improve the roads with the intention of ultimately allowing them to be traveled safely by cars. After the extensive logging by Gould, especially after the 1950 Blowdown, much of the area was occupied by thick low vegetation, the tops of harvested and wind‐thrown trees. Foot travel was difficult. To allow hunters to more easily travel through more remote areas in search of game, Fish and Wildlife staff used a bulldozer to clear and extend logging roads and skid trails to serve as foot trails, starting in the late 1960s. Trails cleared in this way include routes to Mitchell Ponds, Bear Pond, Lost Ponds, Cellar Pond, Beaver Lake, Sly Pond and Squaw Lake, as well as those along Benedict Creek and Butter Brook. A number of routes cleared at that time are now within the West Canada Lake Wilderness, including the trails to Horn Lake and Falls Pond. Many of the cleared routes extended beyond the trails currently marked and maintained. A map prepared by Jack Harnish, a member of the crew that did the trail clearing work, is on file with the Department.

The minutes of the December 9, 1963 Department staff meeting mentioned above included in the list of recommendations for the operation of the area that the Department should establish several small camping areas to include table, fireplace and latrine throughout the area adjacent to the roads where parties can park and camp. By 1965 the Department began constructing campsites and installing fireplaces, picnic tables and privies, which were built in a field just west of the Cedar River entrance. At each suitable location along the road system, a bulldozer was used to make a short access driveway and level an area where a car or pickup truck could park and camp. A number of campsites were created at former log landings. Many of the areas originally intended as roadside parking areas later were converted to campsites. Campsite construction was completed by the late 1960s.

Because of the importance of the Plains as a deer wintering area, the Departments game management staff began studying the area in 1931. Hunting and fishing advocates such as the Adirondack Conservation Council supported the acquisition of the Plains and the development of its roads, trails and campsites for hunting and fishing access. In 1965 and 1966 with federal Pittman‐Robertson Act funding, 30 log landings were graded for hunter parking access and 30,000 trees were planted in the Plains area as an experiment intended to provide winter deer shelter.

In 1965 housing was constructed for the Limekiln and Cedar River gatekeepers. The possibility of a use fee was discussed, but no fee was charged during the early years. During the 1976 season the Department charged a fee of $1.50 or $2.00 per car. A subsequent assessment determined that most of the revenue generated by the fee was offset by the costs of staffing and administration. The fee was discontinued the following year.

Work to clear hunter access trails by bulldozer continued for a few years. However, after repeated incidents of public motor vehicle travel on these trails, 16 barriers were installed in 1970, and motor vehicles no longer were used to maintain the trails. Also in 1970, the original road plan was changed to close 22.5 miles of the original III. Management and Policy Moose River Plains Wild Forest Revised Draft Unit Management Plan/Draft Generic Environmental Impact Statement ‐ July 2010 67 30.5 miles of secondary roads to the public and retain them as administrative roads. The other 8 miles, consisting of the beginning of the Otter Brook truck trail and the road to the Indian River, were upgraded to primary roads and the gate at the Otter Brook bridge was removed.

As work progressed over the years and the condition of the road system improved, the Department relaxed restrictions on the types of vehicles the public could drive. In the late 1960s the Department decided to allow motorhomes up to 22 feet long to travel the roads through big game hunting season, as long as they had tire chains. It was thought that they were less likely to get stuck than vehicles towing camping trailers, which the Department continued to prohibit. However, pressure to allow trailers began early and continued to grow. After Department staff conducted an assessment of the roads and determined that they had been sufficiently improved, they decided to allow trailers beginning around 1980.
For several years after the Department first erected wood signs in the MRPWF, they were repeatedly damaged by black bears. To prevent further destruction, metal signs were installed in 1975.

A detailed Department map prepared in 1977 shows 222 campsite and parking area locations along the road system. The map provides an inventory of the structures at each site, showing the prevalence of fireplaces, picnic tables and privies at the time. Twenty sites were closed in 1980 after the reclassification of the southwestern portion of the area to wilderness, when the road to the Indian River was gated at Indian Lake. The campsites were not given numbers on the ground until the 1980s. A number of original sites that had fallen into disuse were bypassed when the numbers were assigned, so that in 2008 there are 170 numbered sites. In 2006 sites 7, 34, 66, 73, 90, 119a, 130 , and site 1 at Cedar River Flow were modified and designated as accessible sites.
In recent years, maintenance activities have focused on keeping the road system in passable condition, replacing inadequate culverts and trail maintenance. In 2001, four gravel pits were reclaimed and replanted.

In 1996 an engineering evaluation was completed for the public motor vehicle roads in the unit. The report focused on 8 major and 12 minor culvert problem areas and made recommendations for replacing existing culverts with new structures of sufficient capacity to handle a design storm of 100‐year occurrence probability with a snowmelt allowance. Between 2000 and 2005, 11 of the 12 minor sites, with the exception of site 10B, were addressed and site 5A of the major sites is the only one complete. The report and an updated status can be found in Appendix 22.

In 1974, jurisdiction over approximately one acre of State land was transferred from the Hudson River‐Black River Regulating District to the Department for use as a canoe access site on Sixth Lake. In 1986, the Department transferred jurisdiction of 6.41 acres of State land along Sagamore Road to DOT. This parcel encompasses an old sand pit and was transferred so that DOT could relocate their maintenance facility from an area immediately adjacent to State Route 28 to a more screened location. DEC reserved the right to use gravel from this site, as long as it did not interfere with the DOT facility. Currently DOT does not use the site, but may use it at some time in the future.

When the Moose River Recreation Area was first opened to the public, use levels were relatively high. During big game hunting season in 1964, 2,021 vehicles with 5,764 passengers signed in. Though the area originally was purchased and developed for use by hunters, trappers and anglers, the first 10‐day report filed after the 1965 opening on July 1 indicated that 75 percent of visitors were campers and sight‐seers. In 1966, 7,809 people signed in as anglers and 23,408 camper‐days were recorded during big game hunting season, about 6,000 of which were recorded for campsites beyond the Otter Brook bridge. Big game hunters were very successful in the early years, harvesting 373 deer and 15 bear in 1966 and a high of 404 deer in 1968. Deer harvest levels declined sharply after 1969, with 77 harvested in 1970 and 11 in 1971. Since the 1970s the number of deer taken by hunters has increased and in recent years harvest numbers have nearly returned to the levels recorded in the 1960s. The MRPWF remains popular with hunters, trappers and anglers.

Early management included the adoption of a number of regulations in 1972. These regulations, which still apply to public use of the area, require visitors to register at the Cedar River and Limekiln entrances, require the use of tire chains after October 1 except on 4‐wheel drive vehicles, prohibit snowmobile operation during the big game hunting season and prohibit the use of motorcycles and motorized bicycles. Current conditions may warrant the elimination of the registration requirement and the prohibition against motorcycle use.


















































![Old Canal Warehouse in Chittenango [Expires November 19 2023]](https://andyarthur.org//data/photo_005914_large.jpg)

