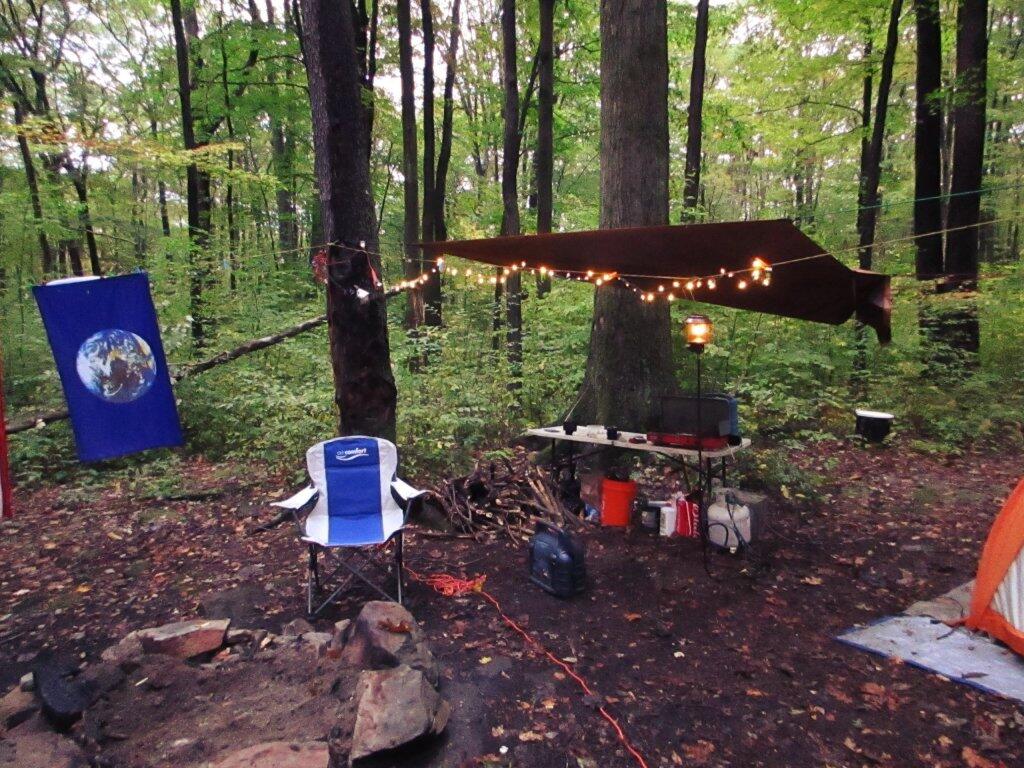
Good Morning! Happy Wednesday. Yes, folks it’s Wednesday. I think this is the first note I’ve done in a few months, but so be it. It really isn’t that hard to do notes, especially now that I’ve switched WordPress, and everything is pretty much standardized and easy to use. It’s a long one, jotted down over the past week,w with lots of things to talk about.
Working on a New WordPress Theme for the Blog. When I brought the blog over to WordPress, my intent was not to create another generic looking WordPress blog, although in many ways that’s how it ended up. I also messed up some of the code, and didn’t build a proper client theme, instead relying on an adapted theme.
The result was a kind of bland mess. The good news is I am now learning how to build a proper client theme on top of an existing, much nicer WordPress theme — that doesn’t look so much like a generic WordPress theme. One of the reasons I avoided for so long going with WordPress, as I didn’t want to end up with a very generic theme. But somehow it all ended up that way. I think the new theme I am going to — based on the popular Pinboard theme is much nicer.
Hopefully it will be up by the start of September, if all goes well. New maps up are on the blog today.

Heading Up to the Northern Half of Green Mountains this Weekend. Probably leave Friday after work, first camp in the Southern Green Mountains near Somerset Reservior, then head North on Vermont 100. There looks to be a lot of neat places to see in the northern Green Mountains, and some spectular scenery.
Plan to stay for a long weekend, by also taking off Monday and Tuesday, which promise to be pretty nice weather. As I don’t really know the area, a lot of the trip will be about seeing what is up there, and going from there to figure out what to do. I will bring the kayak and camera, and certainly are keeping my mind open to taking a nice hike somewheres. They are talking about a continuation of the recent low-humidity, temperate climate weather over the weekend, especially as we head into Monday and Tuesday. Supposed to be some good meteor showers.
I’ve decided to do more of these long weekends, rather then take any full weeks off this summer. I guess you could say the July 4th week was technically a week off, although actually July 4th and July 5th were holidays at the office, so they didn’t really count.
I might take a week-long trip in October to Western NY and Pennsylvania during peak foliage season. That said, I also want to do an extended weekend trip to Moose River Plains and also Lake Kushaqua/Jones Pond and recently re-opened Loon Mountain firetower.
Going to Put Off Getting the Lift-Kit Installed Until at Least March. Originally the plan was to have a lift-kit installed on my truck in October. But after giving it more thought, and carefully reviewing the options, I’ve decided the best option is to wait another six months or so. For one, I want to wear down the stock tires more, so I’m not wasting them as much, and also so I’m a bit closer to end of the factory warranty — the lift kit isn’t covered by the truck’s factory warranty, and while it wouldn’t invalidate the whole warranty, certainly any damage (as unlikely as it is) it could cause wouldn’t be warrantied.
But the other part of the rational is partly money-wise, and because I’m not totally sold on the lift-kit idea. I’ve thought about getting a snowmobile instead this winter, and have been looking at Want Ad Digest. That said, the more I look at it, the more I am not in a rush to get a snowmobile. As much fun as it would be to get deep in the back country in winter — assuming there are groomed trails back there — I worry about break downs and the alike. Not to mention, snowmobiles use a lot of gas, and really aren’t much more efficient then automobiles, because the snow drags them down.
The money-wise issue comes in that things are more expensive then I first estimated a year ago. I think I am going to go with 35s and a 6″ lift kit from a good brand like BDS. Any bigger then that isn’t cost-effective, and non-pratical. That will get me up high enough. The final increase in the height of the truck will be something like 8 inches, because the 35s are 4 inches larger in diameter then factory 31s, and a six-inch lift is half foot higher.

I also think I will go for full-leaf replacements in the back rather then add-a-leafs, to ensure the weight of the camper shell and equipment in the back won’t cause the nose to be pointing in the air, etc. Going to have it re-geared to save fuel, add some more power, not kill the engine or tranny. And there are some other things like the narrower brake lines that are recommended, among other parts, I would probably spring for when it comes to lift-kit. Plus all that labor cost, which will easily be a grand on it’s own.
I want to ride up higher. I am a tall guy. It also will give me a chance to “freshen” up the look of my truck, which after 2 1/2 years will be getting kind of boring and old. I want something I can get 10 years or more out of without getting totally bored with. After I do the lift kit, there are other projects for future years, such as getting the rocker panels Line-X’d, and replacing the bumpers with those awesome Ranch bumpers, that can actually be used for parallel parking without being damaged.
Or maybe I’ll find other toys to spend my money on. It’s good having some extra disposable money kicking around, as I’m sure future jobs won’t nearly pay as much.
Been Reading and Watching More Videos About Getting Off the Grid. Being somebody who camps most weekends from April to November in the back of my pickup truck, and relies heavily on my inverter and the deep cycle battery to keep things lighted up all evening long. I cook my own food in the woods, clean dishes using bottled water, burn my garbage, and dig a whole in woods when I need to go to the bathroom. Heck, with my laptop and the wireless card, I can be up in woods and surfing the web, doing work, and even fielding calls over my cellphone.
I have a pretty decent working understanding of electricity, and how all the off-the-grid thing too. I grew up in the country, are comfortable in woods, and know how to build a good fire in woodstove. I am fascinated to learn more about some of the relatively inexpensive and simplistic living arrangement many-off-the-griders live with, without all costs and hassles of an on-grid house.
My grandfather had one of those absorption-cooler refigerators/freezers in his RV at his campsite in Warrensburg. They’re neat, as one needs more then just a cooler when you live somewhere permanently, rather then wondering the wilderness in your pickup truck. They burn like 5-10 gallons of propane a month. But there also is these high-efficiency refrigerators that are electric and have a lot of insulation, so they don’t strain batteries in a PV/micro-hydro/wind system as much.
But a bigger issue for me is the ability to take showers and get cleaned up properly wherever I live. For that purpose, there are amazingly small tankless-water heaters that use a small amount of propane, but can get water very hot quickly. If you think small, you don’t really need that much flow, compared to a full-scale modern house with a massive-tanked water heater. Hot showers, and hot water for dishes is a necessity to keep clean. If I can get away with it from the code inspectors, I’d be fine with composting toilets or even just a plain old outhouse. That’s a luxury in woods.
Woodstoves, radiant flooring, and other familiar technology is self-explanatory. Having good insulation is a must in this part of the country. I don’t want to have trash pickup — I’m happy enough burning what can be burnt, and taking the glass and metals for proper recycling in the normal industrial fashion.
I like small houses. Smaller is better. I would rather spend my money on land, that could not only be used for recreation like riding quads, shooting guns, and hunting, but also for money by grazing livestock and timber. I am not a greeny, I don’t got a problem with using styrofoam plates for dinner and disposing them in an open fire. I just hate the whole upper-middle class, fancy house living style in the suburbs.
All this reading library books gots me thinking …
But for now I’m fine. As a transition though, I think I would next like to live in a small, handsome, downtown, one that is walkable to a bar and a store, but also provides ample-off-street parking. I think it would be a lot of fun to have an apartment on the second or third floor, above a shop, and be able to sit out and look at my window and watch the traffic go by.
Anywhere I live, I want to be near a National Forest or State Forest that allows free, primitive camping, in a remote-roadside fashion. Not to mention scenic vistas, places to hunt, fish, hike, and spend time outdoors. But I really want to get out of New York, at least eventually. I think it would be fun to own an AR-15, and eventually get a concealed carry permit from a must-issue state, without any pesky questions about whatever stupid things I did decades ago back in college — that hurt nothing but folks egos. To say nothing of not being in a state that’s totally anti-rural and not into the philosophical nature thing.
Far off I guess. Things aren’t that bad right now.